
Audition (hearing) is accomplished by thejoint activities of the ear, the auditory nerve, and the auditory center.
Thehuman auditory system is divided into peripheral and central parts. Theperipheral auditory system includes the outer, middle and inner ears (see Figure 1). The central auditory system refers to the part of the auditory nervebehind the cochlea until the central temporal lobe of the brain (see Figure 2).We hear sound through both air conduction and bone conduction (see Figure 3).Under normal conditions, sound is transmitted to the inner ear through theauricle, external auditory canal, and middle ear, while sound can also betransmitted directly to the inner ear through skull vibration.
Excerpt: tang hao, shi lijuan, yu li, etal.Signal transduction of sound in the ear and its molecular biologicalmechanism (1) [J].Journal of audiology and speech disorders, 2009,17 (6):612-613.
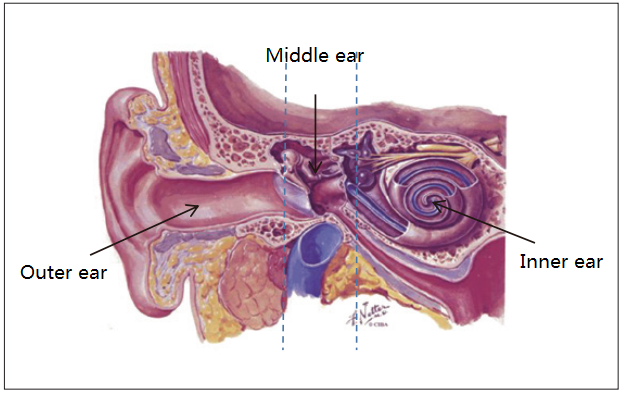
Figure 1
Excerpt: clinical audiology, 5th edition
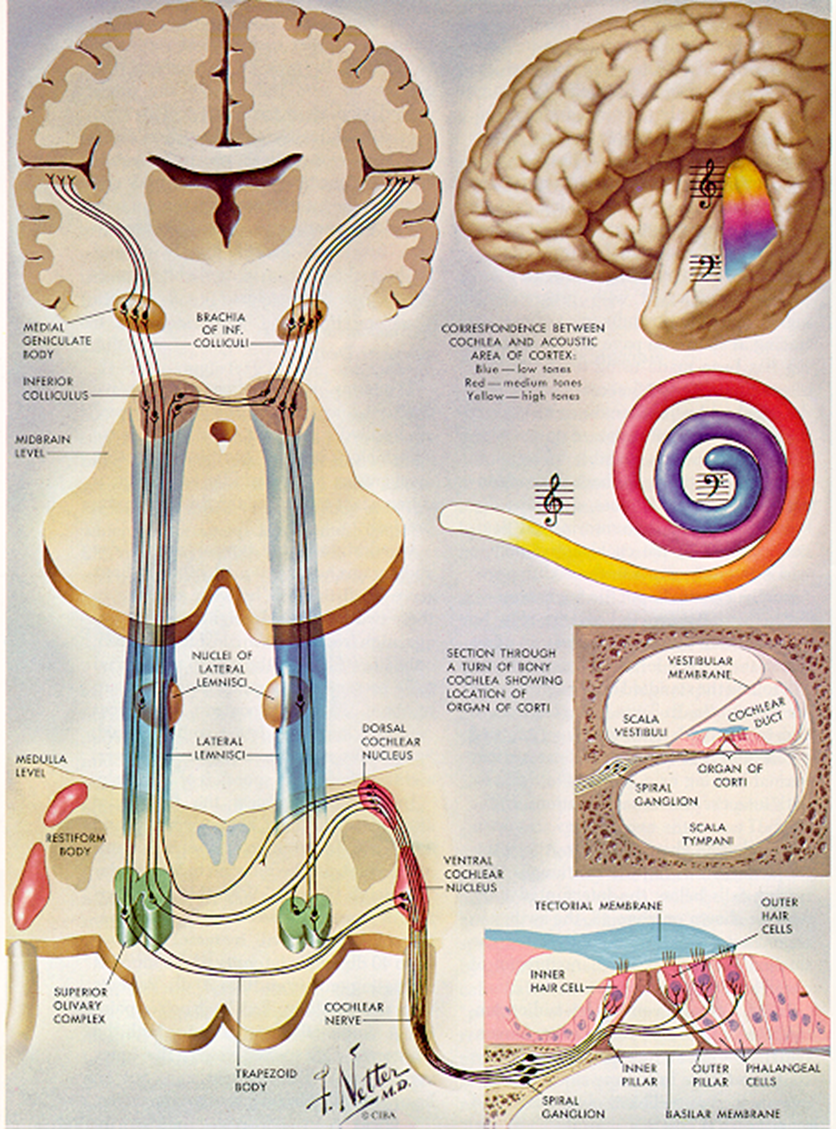
Figure 2
Excerpt: clinical audiology, 5th edition
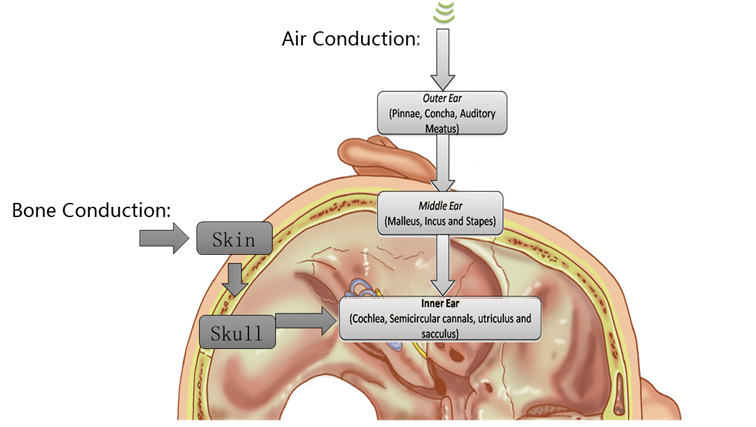
Figure 3
Excerpt: clinical audiology, 5th edition